Services

NABL Certified Labs

Trusted by
1 M+ customers

4.8 / 5 Google rating
Prior Appointment Test
Our streamlined healthcare approach integrates cutting-edge technology, personalized care plans, and expert consultations for optimal wellness outcomes.
1
Choose Medical Specialist
Select expert medical specialist for personalized, optimal care.
2
Choose Consultation Service
Schedule expert consultation for personalized guidance.
3
Make an Appointment
Schedule an appointment easily for timely medical care.
4
Get Diagnosed
Receive an accurate diagnosis for effective treatment plan
1
A diagnostic procedure using X-rays to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes for abnormalities or blockages.
2
High-frequency sound waves to generate images of internal body structures, assisting in the diagnosis and monitoring.
3
A non-invasive ultrasound imaging technique used to assess the structure and function of the heart in real-time.
1
A diagnostic procedure using X-rays to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes for abnormalities or blockages.
2
High-frequency sound waves to generate images of internal body structures, assisting in the diagnosis and monitoring.
4
The insertion of a flexible tube with a camera into the body to visually examine internal organs or tissues.
5
To assess heart function by monitoring the heart’s response to physical stress induced by walking on a treadmill.
6
To restore movement and function through tailored exercises and manual therapy techniques.
5
To assess heart function by monitoring the heart’s response to physical stress induced by walking on a treadmill.
6
To restore movement and function through tailored exercises and manual therapy techniques.
full fledged laboratory
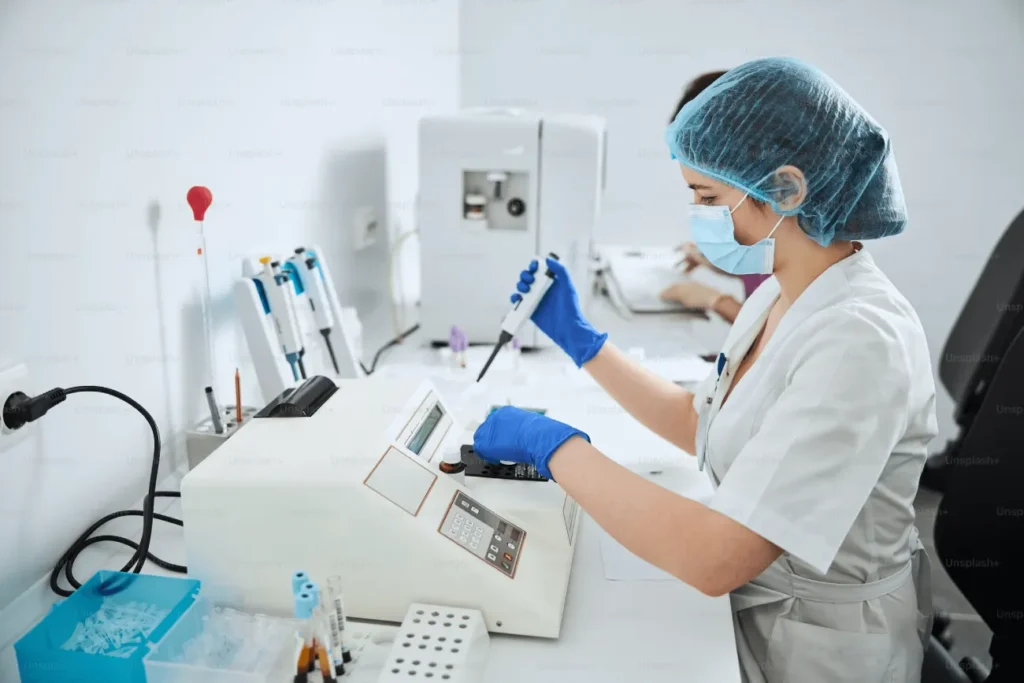

A full-fledged laboratory is a highly equipped facility designed to support various scientific experiments, research, and analyses. It typically includes advanced instruments, safety equipment, and specialized areas for different types of work, such as chemical synthesis, biological testing, and physical measurements. Laboratories are staffed by skilled technicians and scientists who follow strict protocols to ensure accuracy and safety. These environments also have robust systems for data collection and analysis, allowing for detailed study and documentation of results. Additionally, they often adhere to regulatory standards to maintain quality and reliability in their operations.
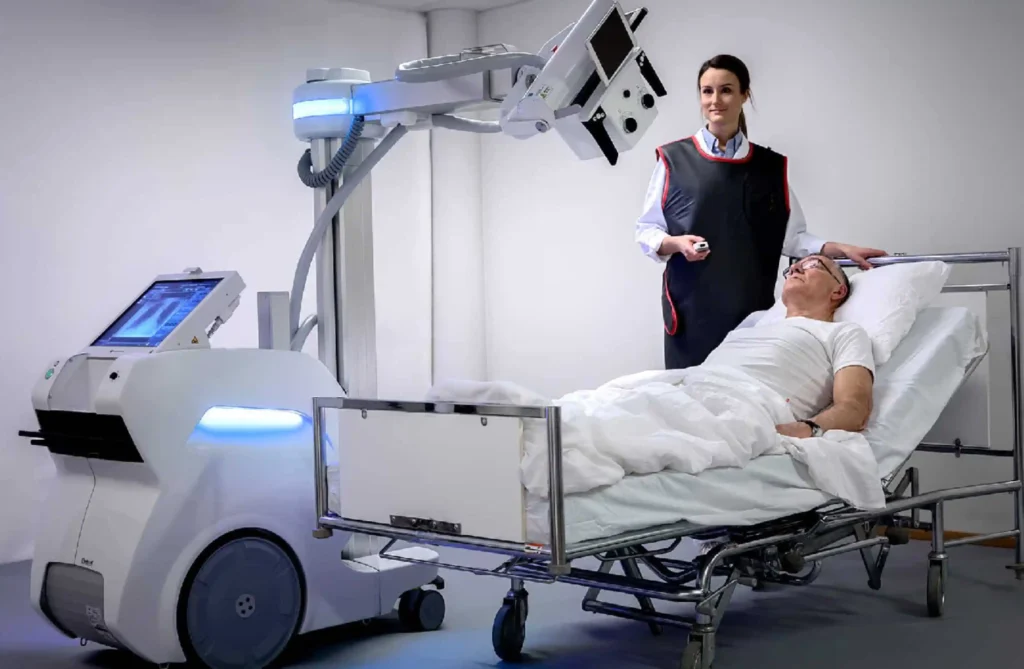


digital X-ray

A digital X-ray is a modern imaging technique that captures X-ray images electronically rather than on traditional film. This technology offers numerous advantages, including faster processing times, reduced radiation exposure, and the ability to enhance and manipulate images for better diagnostic accuracy. Digital X-rays are easily stored and shared electronically, facilitating quick consultations and remote diagnosis. The high-resolution images produced enable more precise detection of medical conditions. Additionally, digital X-ray systems often integrate with other healthcare IT systems, streamlining workflow and improving overall patient care.
ECG
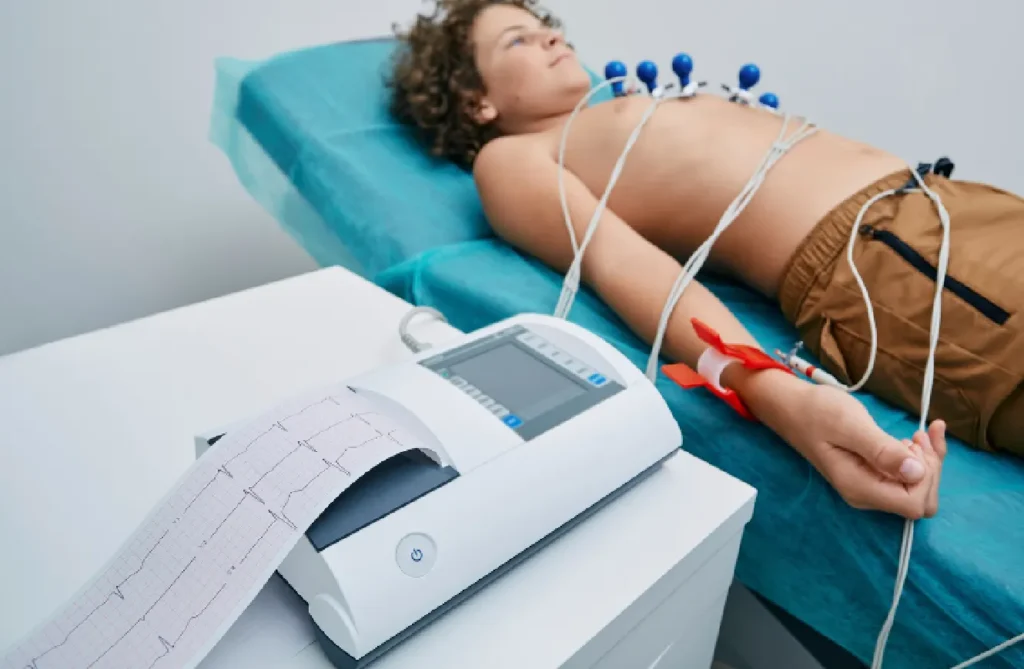
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a medical test that records the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on the skin. It is a crucial tool for diagnosing various heart conditions, such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac abnormalities. The ECG provides a visual representation of the heart’s rhythm and electrical impulses, displayed as waves on a graph. This non-invasive procedure is quick, painless, and widely used in both emergency and routine clinical settings. By analyzing the patterns and intervals of the ECG tracings, healthcare professionals can assess heart health and guide treatment decisions. Advanced ECG machines often come with digital capabilities, allowing for efficient storage, analysis, and sharing of patient data.

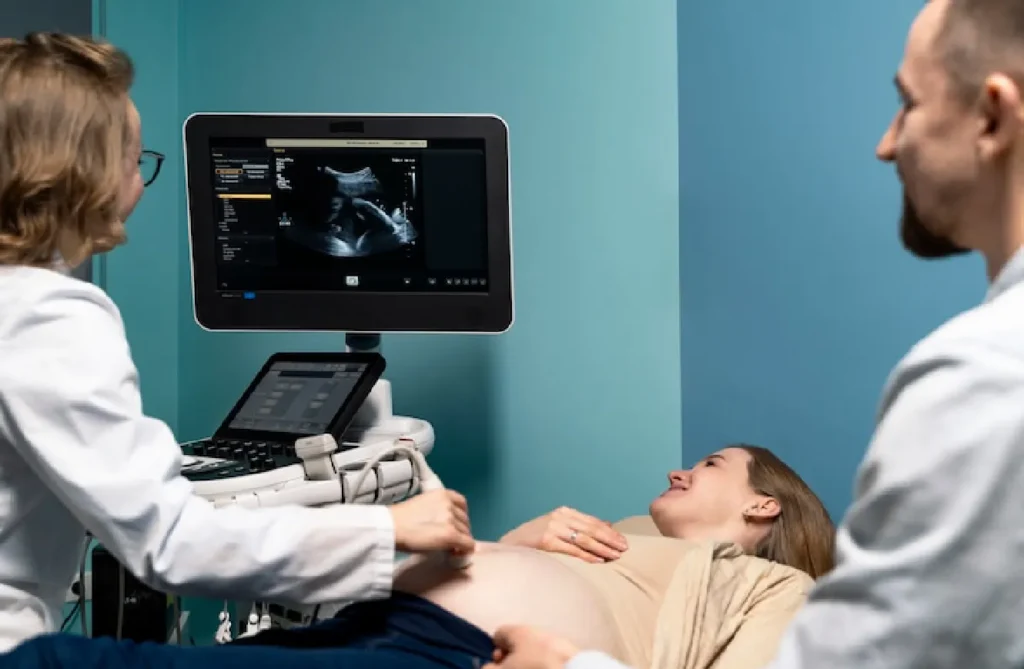
ultra sound scanning

Ultrasound scanning, or sonography, is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the inside of the body. This non-invasive procedure is commonly used to visualize organs, tissues, and blood flow, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of various medical conditions. During the scan, a transducer emits sound waves that bounce off internal structures, creating echoes that are then converted into real-time images on a monitor. Ultrasound is particularly valuable in obstetrics for monitoring fetal development, as well as in cardiology, gastroenterology, and musculoskeletal assessments. The technique is safe, painless, and does not involve ionizing radiation, making it suitable for frequent use. Advanced ultrasound technology allows for detailed 3D and 4D imaging, enhancing the accuracy and scope of diagnostic capabilities.
physiotherapy
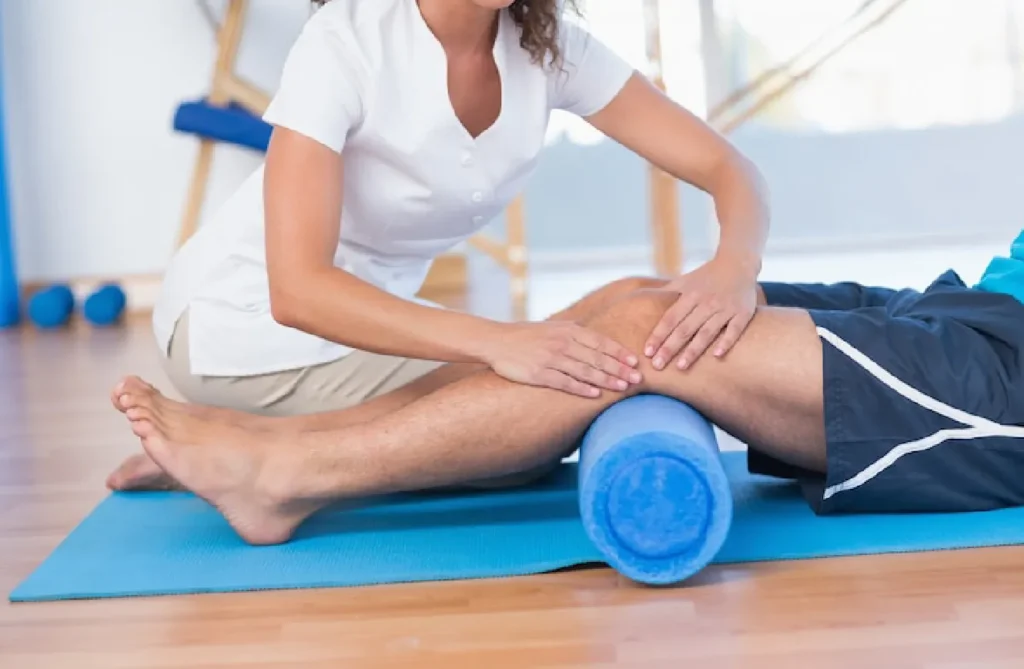

Physiotherapy, or physical therapy, is a healthcare profession focused on diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal and movement disorders through physical methods. These methods include exercises, manual therapy, education, and modalities like heat, cold, and electrical stimulation. Physiotherapists work with patients to improve mobility, strength, and function, aiming to alleviate pain and prevent further injury. This treatment approach is beneficial for a wide range of conditions, from sports injuries and chronic pain to post-surgical rehabilitation and neurological disorders. By promoting movement and functional ability, physiotherapy enhances the quality of life for individuals across all ages. Personalized treatment plans are developed based on the specific needs and goals of each patient, ensuring optimal outcomes.

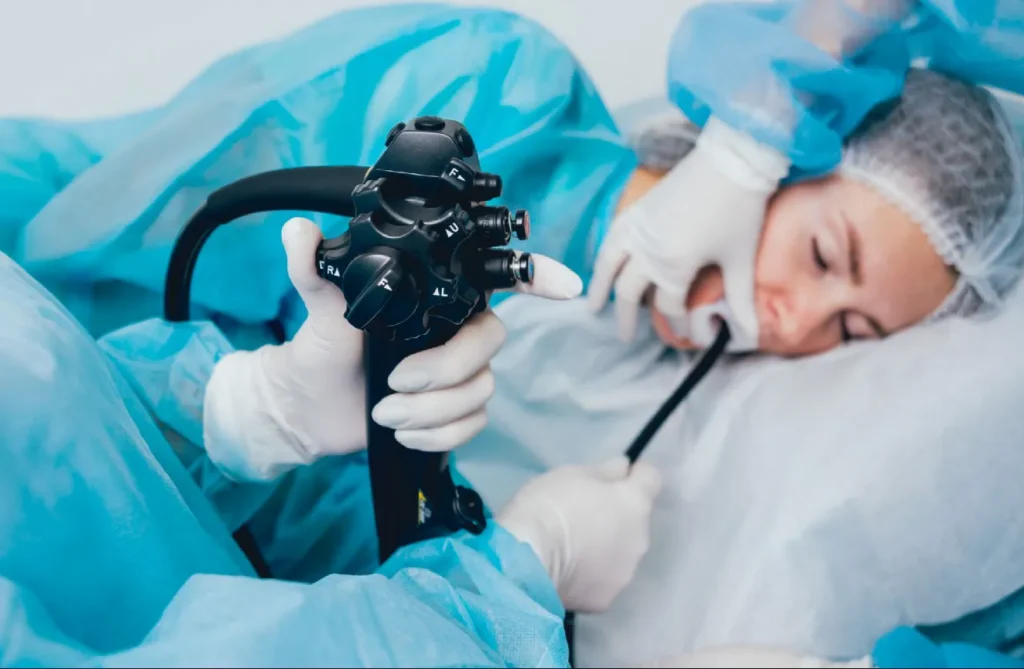
endoscopy

Endoscopy is a medical procedure that involves the use of a flexible tube with a light and camera, called an endoscope, to examine the interior surfaces of an organ or tissue. This minimally invasive technique allows doctors to diagnose and treat conditions within the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system, and other hollow organs without major surgery. During the procedure, the endoscope is inserted through a natural opening, such as the mouth or rectum, providing real-time images displayed on a monitor. Endoscopy can detect abnormalities like ulcers, tumors, inflammation, and bleeding, and also allows for biopsies and certain treatments to be performed on the spot. The procedure is generally safe, with a quick recovery time, and significantly enhances the ability to diagnose and manage various medical conditions accurately and effectively.
PFT
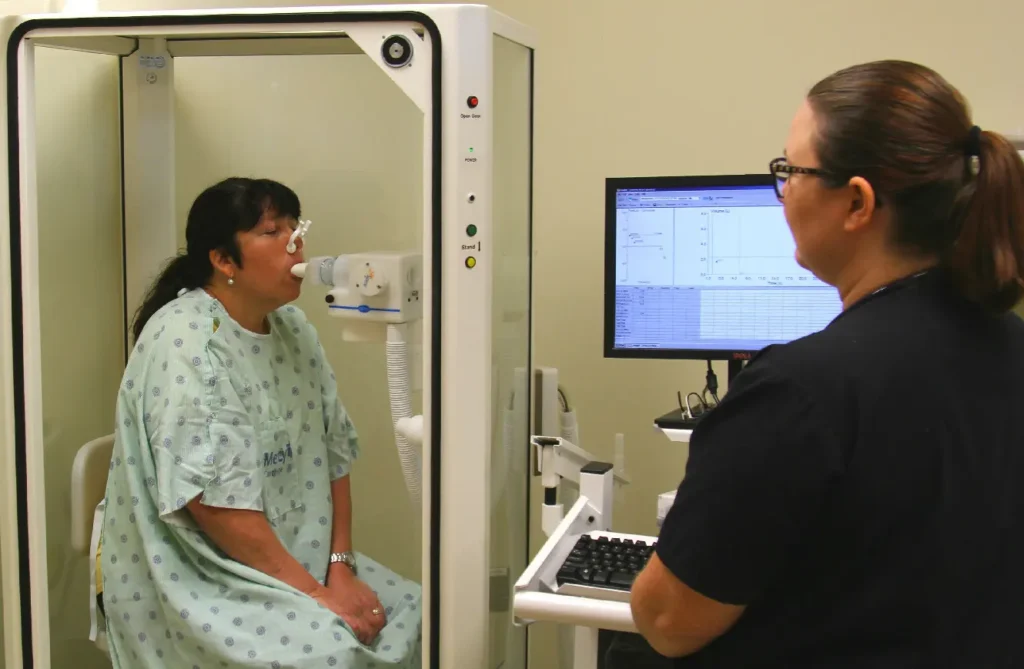

Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) are a series of non-invasive tests that measure how well the lungs are working. These tests assess lung volume, capacity, rates of flow, and gas exchange to help diagnose and monitor respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pulmonary fibrosis. PFTs typically include spirometry, which measures the amount and speed of air a person can inhale and exhale, and may also involve tests like plethysmography and diffusion capacity. By analyzing these parameters, healthcare providers can evaluate the severity of lung dysfunction and tailor treatment plans accordingly. PFTs are essential tools in both clinical and research settings, providing critical information to enhance patient care and understanding of respiratory health.

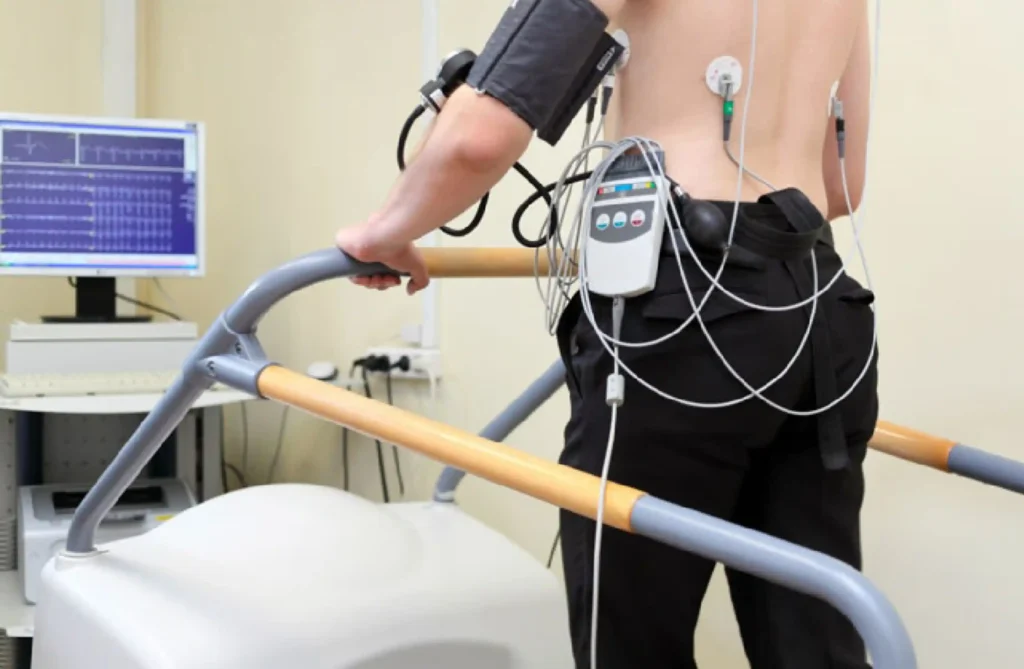
TMT

A Treadmill Test (TMT), also known as an Exercise Stress Test, is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate the heart’s response to physical exertion. During the test, a patient walks or runs on a treadmill with gradually increasing intensity while their heart rate, blood pressure, and electrocardiogram (ECG) are continuously monitored. The TMT helps detect coronary artery disease, assess exercise tolerance, and identify abnormal heart rhythms that may not be apparent at rest. This test is particularly valuable for diagnosing conditions like angina and for assessing the effectiveness of cardiac treatments or interventions. By simulating the heart’s workload during exercise, the TMT provides essential insights into cardiovascular health and helps guide appropriate medical management.
Health Packages

Health packages offer comprehensive medical services tailored to individual needs, providing preventive and diagnostic care. These packages often include routine check-ups, blood tests, imaging scans, and specialist consultations. Designed for various age groups and risk factors, they ensure early detection and management of health issues. Many health providers customize these packages to address specific conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. By bundling services, health packages offer convenience and cost savings compared to purchasing services individually. They play a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being and promoting proactive health management.


